इस पोस्ट में Change the Narration की पूरी जानकारी विस्तारपूर्वक दी गई है। इसके हर एक छोटे से छोटे point को इस पोस्ट में विस्तार से बताया गया है और साथ ही साथ बहुत सारे Examples भी दिए गए हैं ताकि आपको अच्छे से समझ आ सके। इसलिए इस पोस्ट को ध्यान से पढ़ें और समझने का प्रयास करें।
Narration को Direct and Indirect speech भी कहा जाता है। हिंदी में इसे प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन कहते है। किसी की कही गई बात को किसी और को बताना ही Narration कहलाता है। किसी व्यक्ति के द्वारा कही गई बात को दो प्रकार से व्यक्त किया जा सकता है-Direct Speech के द्वारा और Indirect Speech के द्वारा।
1. Direct speech -जब किसी वक्ता के शब्दों को ज्यों का त्यों बिना किसी प्रकार का परिवर्तन किये कहा जाता है, उसे Direct speech या Direct Narration कहा जाता है। Direct Speech के शब्दों को Inverted commas (“……”) के अंदर लिखते हैं।
2. Indirect speech-जब वक्ता के द्वारा कही हुई बात को ज्यों का त्यों न लिखकर हम अपने शब्दों में बयां करते है तो वह Indirect speech कहलाती है। Eg.-
Direct Speech- She said, ” I am working now.”
Indirect Speech- She said that she was working then.

Parts of Direct Speech or Narration
Direct Speech के दो भाग होते हैं ; Reporting speech तथा Reported Speech
Reporting speech- Inverted commas से बाहर वाले वाक्य को Reporting Speech कहते है और इस वाक्य में प्रयुक्त Verb को Reporting Verb कहा जाता है। जैसे-
He said to me,” I am busy.”
इस sentence में ‘He said to me’ Reporting Speech है।
Reporting Speech के Part
He- reporter
said to-reporting verb
me- object of reporting verb
Reported Speech: Inverted commas के अंदर आए हुए वाक्य को Reported Speech कहते है। जैसे-
She said, ” I am learning English.”
ऊपर दिए गए sentence में ‘I am learning English.’ Reported Speech है।
Verb of the Reported Speech
Reported speech में प्रयुक्त verb को verb of the Reported Speech कहा जाता है। जैसे-
He said, ” I am ready.”
इस sentence में ‘am’ Verb of the Reported Speech है।
Indirect Speech- जब हम किसी के द्वारा कही गई बात को हम अपने शब्दों में बयां करते हैं तो वह Indirect speech या Indirect Narration कहलाती है।
Eg. 1. He said, ” I live in Delhi.”
2. He said that he lived in Delhi.
2nd sentence को Indirect speech में लिखा गया है तथा inverted commas का प्रयोग नहीं किया गया है।
Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
(Rules of Change the Narration)
1. Reporting Speech में Change
Inverted commas के बाहर का part Reporting Speech कहलाता है। इसमें प्रयुक्त verb को change करने के नियम निम्नलिखित है-
Say to-tell
Says to- tells
Will say to- will tell
Said to- told
यदि वाक्य में say, says तथा said के बाद to न आए तो इन्हें Indirect Speech में ज्यों का त्यों लिखते हैं।
Note: ‘say’ एक ऐसी verb है जो अपने बाद कभी भी indirect object ( human being) को नहीं रख सकती। इसीलिए इसके बाद ‘to’ Preposition लगानी पड़ती है ताकि हम इसके बाद indirect object को लगा सके। लेकिन ‘tell’ verb human being को object रख सकती है। Tell एक Di transitive verb है। ये अपने साथ दोनों type के object रखती है। Indirect भी और Direct भी।
2. Commas में change
Assertive sentence को Direct से Indirect speech में बदलते समय Inverted commas को हटाकर that लिखते है। जैसे-
Direct: You say, “I work hard.”
Indirect: You say that you work hard.
Change of Pronouns (सर्वनाम के परिवर्तन)
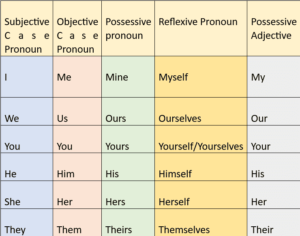
Rules for Change of Pronouns
1 2 3
↓ ↓ ↓
S O N
1-First person(I,we) of the Reported Speech
2-Second person(you) of the Reported Speech
3- Third person(he, she, it, they, any name) of the Reported Speech
S-Subject of the reporting verb
O- Object of the reporting verb
N- No change
Rule 1: The First-person pronouns of the reported speech are changed according to the subjects of the reporting verbs.
Reported speech के 1st person pronouns को Reporting Speech के subject के ‘pronoun’ के अनुसार बदला जाता है।
For example –
Direct: You said, “I have done my work.”
Indirect: You said that you had done your work.
Direct: He said, “I have done my work.”
Indirect: He said that he had done his work.
Rule 2: The Second-person pronouns of the reported speech are changed according to the objects of the reporting verbs.
Reported speech के 2nd person pronouns को Reporting Verb के Object के ‘ pronoun’ के अनुसार बदला जाता है।
For example –
Direct: He said to me, ” You do it well.”
Indirect: He told me that I did it well.
Direct: My teacher said to me, “You need an atlas.”
Indirect: My teacher told me that I needed an atlas.
Rule 3: The Pronouns of the third person remain unchanged.
Reported speech के 3rd person pronouns अपरिवर्तित रहते हैं।
For example –
1. Direct: He says to me, “He will go to Kolkata.”
Indirect: He tells me that he will go to Kolkata.
2. Direct: My father said, “He has bought a new car “
Indirect: My father said that he had bought a new car.
Rules for Changes of Tenses in Indirect Speech
Rule 1: If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future tense, the Tense of the Verb in the reported speech remains unchanged.
अगर ‘Reporting verb’ present या future tense में हो तो Reported Speech के Tense में कोई change नहीं होता।
For example –
1. Direct: He says, ” I want a book.”
Indirect: He says that he wants a book.
2. Direct: My father will say, ” Books have become very costly.”
Indirect: My father will say that books have become very costly.
3. Direct: He says to me, ” You have not returned my book.”
Indirect: He tells me that I have not returned his book.
Rule 2: If the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the Tense in the Reported Speech is changed according to the given table.
यदि ‘Reporting Verb’ past tense में है तो ‘Reported Speech’ का Tense नीचे दी गई Table के अनुसार बदला जाता है।
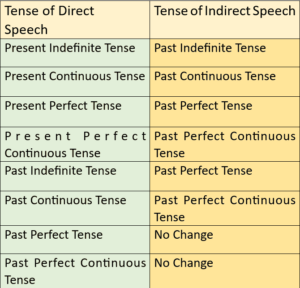
Examples:
1. Direct: The girl said, ” I have a pet.”
Indirect: The girl said that she had a pet.
2. Direct: Nikhil said, “My father is sleeping.”
Indirect: Nikhil said that his father was sleeping.
3. Direct: Ananya said, ” I have finished my project work.”
Indirect: Ananya said that she had finished her project work.
4. Direct: She said, “I have been studying all day.”
Indirect: She said that she had been studying all day.
5. Direct: Veena said, “I bought fresh vegetables from the market.”
Indirect: Veena said that she had bought fresh vegetables from the market.
6. Direct: Divya said to me, “I was cooking dinner.”
Indirect: Divya told me that she had been cooking dinner.
7. Direct: Hardik said, “I had switched off the light.”
Indirect: Hardik said that he had switched off the light.
8. Direct: He said, “I had been waiting for hours.”
Indirect: He said that he had been waiting for hours.
Note: 1. यदि Reporting Speech का object न दिया गया हो तथा Reported Speech का Subject ‘you’ हो तो हम ‘to me’ को ही Reporting Speech का object मान कर चलेंगे।
2. अगर ‘Main clause’ past में हो तो ‘Sub clause’ को भी past में लिखते है।
3. अगर ‘Reporting Verb’ present या future में है तो ‘Reported speech’ का Tense कभी change नहीं होगा क्योंकि काम अभी तक हुआ नहीं है; वह होगा इसीलिए इस काम को हम हमेशा ‘Present’ में लिखते है। जैसे-
The man said, “You are trying to make it worse for me.”
The man said that I was trying to make it worse for him.
4. Reporting speech के objective part में जो भी आता है चाहे वो adverb हो या कोई Time Indication हो; वह हमेशा as it is रहता है। अगर ये सब Quotation Marks के अंदर लिखा होता तो change हो जाता।
For example-
Sahil said to his brother yesterday, “I want to have a party tonight.”
Sahil told his brother yesterday that he wanted to have a party that night.
अगर ‘ yesterday ‘ Inverted commas के अंदर लिखा होता तो उसे ‘the previous day’ में change कर दिया जाता।
She said, “When I was a child, I wasn’t afraid of ghosts.”
She said that when she was a child she wasn’t afraid of ghosts.
Note- इस sentence में was को had been में नहीं बदला जाएगा क्योंकि दोनों बातें एक ही समय के लिए बोली जा रही है। जब वह बच्ची थी तबही भूत से डरती थी। इसमें कोई एक काम दूसरे से आगे या पीछे नहीं हो रहा।
Rule 3. यदि ‘Reporting Speech’ past tense में तथा Reported Speech ‘Future tense’ में हो तो नीचे दी गई Table के अनुसार परिवर्तन किये जाते हैं।

Examples:
1. Direct: Ragini said to me, “I shall play with you.”
Indirect: Ragini told me that she would play with me.
2. Direct: She said, “I will go to Delhi.”
Indirect: She said that she would go to Delhi.
3. Direct: Kamal said to Simran, “You will be driving your car.”
Indirect: Kamal told Simran that she would be driving her car.
4. Direct: She said to her friend, “I will have cooked the food.”
Indirect: She told her friend that she would have cooked the food.
5. Direct: Neha said, “I will have been travelling to Delhi tomorrow.”
Indirect: Neha said that she would have been travelling to Delhi the next day.
Other Verb Changes
Rule 1-अगर ‘Reporting Speech’ Past Tense में है तब Reported Speech में दी गई Auxiliary Verbs को नीचे दी गई Table के अनुसार Indirect Speech में बदलते हैं।

Examples:
1. Direct: Sahil said, “I can play the flute well.”
Indirect: Sahil said that he could play the flute well.
2. Direct: Ravi said, “I may return sooner than expected.”
Indirect: Ravi said that he might return sooner than expected.
3. Direct: Riya said to her friend, “I have to carry the lunch box with me.”
Indirect: Riya told her friend that she had to carry the lunch box with her.
4. Direct: The doctor said, “I am always busy.”
Indirect: The doctor said that he was always busy.
5. Direct: The soldiers said, “We are heroes.”
Indirect: The soldiers said that they were heroes.
6. Direct: My teacher said, “Reema was a good student.”
Indirect: My teacher said that Reema had been a good student.
7. Direct: She said, “I have a nice dress “
Indirect: She said that she had a nice dress.
8. Direct: Anjali said to her friend, “I do my work on time.”
Indirect: Anjali told her friend that she did her work on time.
9. Direct: Sarika said to me, “You have beautiful handwriting.”
Indirect: Sarika told me that I had beautiful handwriting.
10. Direct: Hardik said, “I am not scared of creepy crawlies.”
Indirect: Hardik said that he was not scared of creepy crawlies.
Rule 2- Used to, Dare, Should, Ought to, Would, Had better, Need, Might तथा Would rather- इन सभी Verbs को Indirect Speech में ज्यों का त्यों लिखा जाता है। इनमें कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता।
Examples:
1. Direct: My teacher said, “She used to paint very well.”
Indirect: My teacher said that she used to paint very well.
2. Direct: My teacher said, “You all must participate in sports and extracurricular activities.”
Indirect: My teacher said that we all must/had to participate in sports and extracurricular activities.
Change of Words Denoting Nearness ( Time and position)
When we change direct speech into indirect, some words denoting nearness of time or position are changed into suitable words denoting distance. This change is made if the reporting verb is in the past tense.
जब हम Direct Speech को Indirect speech में बदलते है तो समय या स्थिति की निकटता को दर्शाने वाले कुछ शब्द दूरी को दर्शाने वाले उपयुक्त शब्दों में बदल जाते हैं। यह परिवर्तन तब किया जाता है जब ‘Reporting Verb’ भूतकाल में हो।

Examples:
1. Direct: He said, “I am feeling out of sorts today.”
Indirect: He said that he was feeling out of sorts that day.
2. Direct: Sonam said, “I may go to Indore tomorrow.”
Indirect: Sonam said that she might go to Indore the next day.
3. Direct: She said, “Father will have reached home by now.”
Indirect: She said that father would have reached home by then.
4. Direct: Rohit said, “We can play here in the evening.”
Indirect: Rohit said that we could play there in the evening.
5. Direct: Monika said, “Father will be leaving for a medical conference next week.”
Indirect: Monika said that father would be leaving for a medical conference the following week.
6. Direct: They said, “We saw this beautiful waterfall two days ago.”
Indirect: They said that they had seen that beautiful waterfall two days earlier.
7. Direct: He said, “I am glad to be here this evening.”
Indirect: He said that he was glad to be there that evening.
Important Rules to Change the Narration
1. यदि ‘Reporting Verb’ past tense में है तथा ‘Reported Speech’ में कोई Universal Truth, habitual fact, Historical Truth or Event, Proverb आदि दी हो तो Indirect Speech बनाते समय ‘Reported Speech’ के Tense में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं किया जाता है।
If ‘Reporting Verb’ is in past tense and any Universal Truth, Habitual fact, Historical Truth or Event, Proverb, etc. is given in ‘Reported Speech’, no change is made in the tense of ‘Reported Speech’ while making Indirect Speech.
Examples:
Universal Truth
1. Direct: My teacher said, “The earth moves around the sun “
Indirect: My teacher said that the earth moves around the sun.
2. Direct: My science teacher said, “Gravitational force pulls objects towards the earth.”
Indirect: My science teacher said that gravitational force pulls objects towards the earth.
Habitual fact
Direct: My grandfather said, “Teenagers are impulsive.”
Indirect: My grandfather said that teenagers are impulsive.
Direct: Palak said, “Father watches the late night news before going to bed every night.”
Indirect: Palak said that Father watches the late night news before going to bed.
Historical Truth
Direct: My father said, “India got freedom in 1947.”
Indirect: My father said that India got freedom in 1947.
Direct: Direct: The teacher said to us, “The Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan.”
Indirect: Indirect: The teacher told us that the Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan.
Proverb
Direct: My mother said to me, “Honesty is the best policy.”
Indirect: My mother told me that honesty is the best policy.
Direct: He said, “All that glitters is not gold.”
Indirect: He said that all that glitters is not gold.
2. यदि ‘Reported Speech’ में clause ‘as soon as, when, while’ आदि से शुरू हो तो Indirect Speech बनाते समय ‘Reported Speech’ के Tense में सामान्यतः कोई परिवर्तन नहीं किया जाता है।
If the clause in ‘Reported Speech’ starts with ‘as soon as, when, while’ etc., Generally no change is made in the tense of ‘Reported Speech’ while making Indirect Speech.
Examples:
Direct: My father said to me, “As soon as the train arrived, I boarded it.”
Indirect: My father told me that as soon as the train arrived, he boarded it.
Direct: He said, “When I came to your house, you were teaching your child.”
Indirect: He said that when he came to his house, I was teaching my child.
3. Direct से Indirect में change करते वक्त sentence का meaning change नहीं होना चाहिए।
The meaning of the sentence should not be changed while changing from Direct to Indirect.
Examples of Assertive Sentences of Change the Narration
Assertive Sentences के अंतर्गत Affirmative sentences तथा Negative sentences आते हैं।
Direct: Nisha said to me, “I have completed the task.”
Indirect: Nisha told me that she had completed the task.
Direct: Shubham said to me, “I saw her yesterday.”
Indirect: Shubham told me that he had seen her the previous day.
Direct: They said, “It was remarkable.”
Indirect: They said that it had been remarkable.
Direct: He will say to them, “I have informed your parents.”
Indirect: He will tell them that he has informed their parents.
Direct: Vijay said, “I am here to help you all.”
Indirect: Vijay said that he was there to help us.
Direct: Aarti said, “I am in a hurry today.”
Indirect: Aarti said that she was in a hurry that day.
Direct: He promised, “I will do it tomorrow.”
Indirect: He promised that he would do it the next day/ the following day.
Conversion of Interrogative Sentences into Indirect Speech
While changing the interrogative sentences into indirect speech, the following rules should be observed:
प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों को ‘Indirect Speech’ में बदलने के लिए निम्नलिखित नियमों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए-
1. The reporting verb ‘said/said to’ in the Direct Speech mode is usually changed into asked.
Direct Speech की reporting verb ‘said/said to’ सामान्यतः ‘asked’ में बदल दिया जाता है।
2. Enquire, demand, wonder, want to know etc. can also be used in place of the reporting verb of direct speech.
Direct Speech की ‘Reporting Verb’ को enquire, demand, wonder, want to know आदि में भी बदला जा सकता है।
3. The interrogative form is changed into the assertive form and the mark of interrogation is dropped.
प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य को सकारात्मक वाक्य में परिवर्तित कर दिया जाता है तथा Interrogation का चिन्ह हटा दिया जाता है।
4. अगर ‘Reported Speech’ Wh word (like who, whom, whose, when, what, where, why) से शुरू हो तो Indirect में change करते समय उसी Wh word को as a conjunction प्रयोग कर लिया जाता है जिससे ‘Reported Speech’ शुरू हो रही है।
If ‘Reported Speech’ starts with a Wh word (like who, whom, whose, when, what, where, why) then while changing into Indirect, the same Wh word is used as a conjunction with which ‘Reported Speech’ is starting.
5. यदि ‘Reported Speech’ की शुरुआत ‘Auxiliary verb’ से हो तो Conjunction ‘if या whether ‘ का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
If reported speech begins with auxiliary verb, conjunction ‘if’ or ‘whether’ is used.
6. Tenses, pronouns and words denoting nearness are changed according to the rules explained earlier.
Tenses, pronouns और nearness denoting words को पहले बताए गए नियमों के अनुसार बदला जाता है।
Examples:
(For Yes or No type of questions)
1. Direct: I said to him, “Will you be late?
Indirect: I asked him whether he would be late.
2. Direct: She said to me, “Are you going to the class?”
Indirect: She asked me if I was going to the class.
3. Direct: He said to me, “Did you break my slate?”
Indirect: He asked me if I had broken his slate.
4. Direct: The lady said to the porter, “Will you take my luggage to the platform?”
Indirect: The lady asked the porter if he would take her luggage to the platform.
5. Direct: The boy said to the teacher, “May I come in, Sir?”
Indirect: The boy respectfully asked the teacher if he might go in.
6. Direct: My mother said to me, “Will your home tutor come today?”
Indirect: My mother wondered if my home tutor would come that day.
Direct: My teacher said to me, “Will you trust such a friend?”
Indirect: My teacher asked me if I would trust such a friend.
8. Direct: Mother said to me, “Have you taken your medicine?”
Indirect: Mother asked me if I had taken my medicine.
9. Direct: Deepak said to his brother, “Have you been playing here for two hours?”
Indirect: Deepak asked his brother if he had been playing there for two hours.
10. Direct: I said to Kavita, “Did you make this mischief?”
Indirect: I asked Kavita if she had made that mischief.
Examples:
( For Wh-word questions)
1. Direct: She said to me, “Who teaches you English?”
Indirect: She asked me who taught me English.
2. Direct: Simran said to me, “Where are you going?”
Indirect: Simran asked me where I was going.
3. Direct: He said to me, “How old are you?”
Indirect: He asked me how old I was.
4. Direct: He said to Sumit, “What do you wish to buy?”
Indirect: He asked Sumit what he wished to buy.
5. Direct: Reena said to me, “When will you go to the fair?”
Indirect: Reena asked me when I would go to the fair.
6. Direct: My friend asked, “How much did you pay for the new iPhone?”
Indirect: My friend enquired how much I had paid for the new iPhone.
7. Direct: My friends said to me, “What gift do you want for your birthday?”
Indirect: My friends asked me what gift I wanted for my birthday.
8. Direct: My cousin asked me, “What do you plan to do after your 12th?”
Indirect: My cousin wanted to know what I planned to do after my 12th.
9. Direct: She said, “Where are your books?”
Indirect: She asked where my books were.
10. Direct: The teacher asked me, “Did you do your holiday homework or not?”
Indirect: The teacher wanted to know whether I had done my holiday homework or not.
Conclusion:
आशा करते है कि आपको ये आर्टिकल अच्छा लगा होगा और इस आर्टिकल की सहायता से आपको Change the Narration को समझने में काफी मदद मिली होगी। अगर आपके मन में कोई सवाल हो तो आप हमें नीचे कमेंट में पूछ सकते है। इस आर्टिकल को आप अपने मित्रों के साथ सोशल मीडिया पर शेयर जरुर करें।
Read More Posts: