इस पोस्ट में Active & Passive voice की पूरी जानकारी दी गई है। जैसे – Active और Passive Voice किसे कहते हैं, इनके वाक्यों की पहचान क्या होती है तथा Active Voice के वाक्यों को Passive Voice में कैसे change किया जाता है और इनके कौन-कौन से Rules और Structures होते हैं। इन सभी चीजों को यहां पर विस्तार से बताया गया है और साथ ही साथ हर type (Affirmative, Negative, Interrogative, W.H Words Sentences etc.) के ढेर सारे Examples भी दिए गए हैं ताकि आपको समझने में आसानी हो सके।

Voice
Voice को हिंदी में वाच्य कहा जाता है। Voice, verb की वह characteristic है जो हमें यह तय करने में मदद करती है कि subject क्या करता है अर्थात किसी sentence का subject , sentence में दी गई verb का doer है या receiver.
Doer of the action किसे कहते है।
यदि किसी वाक्य का कर्ता स्वयं क्रिया का संपादन करता है तो उसे Doer of the action कहा जाता है। जैसे-
वह क्रिकेट खेल रहा है।
He is playing cricket.
मैं अंग्रेजी पढ़ाता हूं।
I teach English.
इन वाक्यों के कर्ता स्वयं क्रिया का संपादन करते हैं अर्थात Doer of the action है।
Receiver of the action किसे कहते है।
यदि किसी वाक्य का कर्ता स्वयं क्रिया का संपादन नहीं करता है बल्कि क्रिया उसपर ही संपादित होती है यानि कि जब कर्ता किए गए कार्य के प्रभाव/असर को Receive करता है तो उसे Receiver of the action कहते है। जैसे-
यहां अंग्रेजी पढ़ाई जाती है।
English is taught here.
उसे डांटा जा रहा है।
He is being scolded.
इन वाक्यों के कर्ता (English, He) स्वयं किसी क्रिया को नहीं कर रहे बल्कि क्रिया उन पर ही की जा रही है अर्थात इन वाक्यों के कर्ता किए गए कार्य के प्रभाव को Receive कर रहे हैं।
किसी कथन को दो प्रकार से व्यक्त किया जा सकता है। पहले में, वाक्य के ‘verb’ द्वारा ‘subject’ को प्रधानता दी जाती है तथा ‘verb’ active होता है। दूसरी तरह के वाक्यों में ‘object’ को प्रधानता दी जाती है तथा ‘verb’ passive होता है।
( A statement can be expressed in two ways. In the first, stress is on the subject & verb is active. In the second, stress is on the object & verb is passive.)
Kinds of Voice
Voice दो प्रकार के होते हैं-
(‘Voice’ is of two types)
1. Active Voice
2. Passive Voice
1. Active Voice- जब कार्य Subject के द्वारा किया जाए और इसका प्रभाव Object के ऊपर पड़े तो यह active voice कहलाता है।
(When the work is done by the subject and its effect falls on the object, it is called the active voice.)
2. Passive Voice- जब कार्य का प्रभाव कर्ता के ही ऊपर पड़ रहा हो तो यह passive voice कहलाता है।
(When the effect of the work is falling on the doer only, it is called the passive voice.)
Examples-
Active Voice
1. Birds build nests.
2. The mason is building the wall.
3. The guard opened the gate.
4. This shelf contains books.
Passive Voice
1. Nests are built by birds.
2. The wall is being built by the mason.
3. The gate was opened by the guard.
4. Books are contained in this shelf.
Note- जिस वाक्य का subject, Doer of the action होता है वह वाक्य Active Voice में होता है और जिस वाक्य का subject, Receiver of the action होता है वह वाक्य Passive Voice में होता है।
(The sentence whose subject is Doer of the action is in Active Voice and the sentence whose subject is Receiver of the action is in Passive Voice.)
चूंकि ‘passive voice’ स्थिति को बताती है न कि ‘action’ को, passive voice की मुख्य क्रिया हमेशा ‘be’ form (is, am, are, was, were, has been, have been, had been) में होती है तथा इसके बाद हमेशा V3 होता है।
(Since the passive voice tells the state and not action, the main verb of passive voice is always a form of ‘be’ & it is always followed by V3.)
Passive Voice- Be+ V3 (past participle)
Active Voice से Passive Voice में बदलने के नियम
1. सबसे पहले Active Voice के object को पहचाने।
2. Active Voice के object को passive sentence में subject के स्थान पर रखें क्योंकि Active Voice का subject बन जाता है, object of the passive voice तथा Active Voice का object बन जाता है, subject of the passive voice.
3. Passive auxiliary verb बनाने के लिए ‘to be’ के उचित रूप का प्रयोग करें (जैसे- is, am, are, was, were, has been, have been, had been)
4. Active Voice किसी भी tense का हो , passive voice में हमेशा main verb की third form का प्रयोग किया जाएगा।
5. यदि आवश्यक हो, तो passive voice में एक doer/agent जोड़े ताकि यह पहचाना जा सके कि कार्य किसके द्वारा किया गया है। Preposition ‘by’ के द्वारा agent को दर्शाया जाता है।
6. Active से Passive बनाते वक्त ना तो meaning change होता है और ना ही Tense change होता है।
‘by’ के अलावा at, to, with आदि का प्रयोग भी होता है लेकिन कुछ विशेष शब्दों के बाद।
(1. The first step is to identify the object of the active sentence.
2. Put the object of the active sentence in the subject position in the passive sentence because the subject of Active Voice becomes the object of the passive voice and the object of Active Voice becomes the subject of the passive voice.
3. Use the appropriate form of the verb ‘to be’ (e.g., am, are, was, were, has been, have been, had been) to form the passive auxiliary verb.
4. Active Voice may be of any tense, in passive voice the third form of main verb will always be used.
5. If necessary, add an agent to the passive sentence to identify by whom the work is done. The agent is introduced by the preposition ‘by’.
Apart from ‘by’, at, to, with, etc. are also used, but after some special words.
6. While converting active to passive, neither the meaning changes nor the tense changes.
Apart from ‘by’, at, to, with, etc. are also used, but after some special words.)
Change in Pronouns
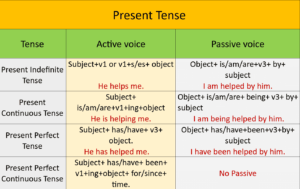
सामान्यत: ‘tense’ के बारह रूपों में से आठ tenses का ही ‘active voice’ से ‘passive voice’ बनाया जाता है। निम्नलिखित ‘tenses’ का ‘passive voice’ नहीं बनता है-
1. Present Perfect Continuous
2. Past Perfect Continuous
3. Future Continuous
4. Future Perfect Continuous
 Examples-
Examples-
Active: My brother likes football.
Passive: Football is liked by my brother.
Active: Palak cooks delicious food.
Passive: Delicious food is cooked by Palak.
Active: I am writing a story.
Passive: A story is being written by me.
Active: They are calling Simran.
Passive: Simran is being called by them.
Active: The rich man has donated his money.
Passive: His money has been donated by the rich man.
Active: Our school team has won the cricket championship.
Passive: The cricket championship has been won by our school team.
Active: She has completed the task.
Passive: The task has been completed by her.
Active: I have learnt the lesson.
Passive: The lesson has been learnt by me.
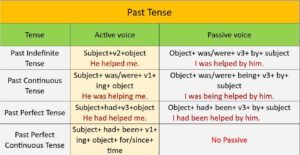 Examples-
Examples-
Active: He broke the glass.
Passive: The glass was broken by him.
Active: The peon opened the gate.
Passive: The gate was opened by the peon.
Active: He was taking tea.
Passive: Tea was being taken by him.
Active: Meenu was cooking the meal.
Passive: The meal was being cooked by Meenu.
Active: Rinku was taking a nap.
Passive: A nap was being taken by Rinku.
Active: They had parked the car.
Passive: The car had been parked by them.
Active: He had taken lunch.
Passive: Lunch had been taken by him.
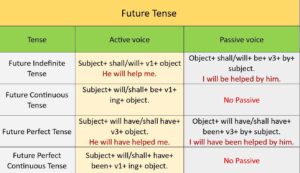 Examples-
Examples-
Active: They will play cricket.
Passive: Cricket will be played by them.
Active: They will ask me several questions.
Passive: I will be asked several questions by them.
Active: He will have written a book.
Passive: A book will have been written by him.
Active: Rahul will have eaten an apple.
Passive: An apple will have been eaten by Rahul.
कैसे पहचाने कि verb के बगल में जो word है वो object है या नहीं-
हम verb से 2 questions पूछेंगे। अगर दोनों में से किसी एक का भी जवाब आ गया तो वो जवाब ही object होगा। अगर जवाब नहीं आया तब verb के बगल वाला word object नहीं होगा।
(We will ask 2 questions to the verb. If the answer to any one of the two is given then that answer will be the object. If the answer is not given then the word next to the verb will not be the object.)
1. Whom (पहला सवाल whom से पूछना है।)
2. What (दूसरा सवाल what से पूछना है।)
Examples-
1. Ragini slapped Nitin.
रागिनी ने किसे थप्पड़ मारा?
जवाब- नितिन को
तो इस sentence में object ‘Nitin’ है।
Riya will eat an apple.
रिया किसको खाएगी?
जवाब- no
रिया क्या खाएगी?
जवाब- an apple
Manisha slept in the room.
मनीषा किसको सोयी? -No answer
मोनिका क्या सोयी?- No answer
इस sentence में verb से whom या what का reply नहीं मिल रहा है इसलिए verb के बाद कोई object नहीं है।
You should come here.
इस sentence में ‘come’ से what या whom का reply नहीं मिल रहा इसलिए इस sentence में कोई object नहीं है। ‘here’ यहां adverb of place है।
My uncle sat on the sofa.
Reena was crying in the kitchen.
My neighbour died in his room.
He will go to Mumbai.
इन सभी sentences का भी passive possible नहीं है क्योंकि इन सभी से what या whom का reply नहीं मिल रहा है।
Note- जब कोई action अपने आप हो जाए; उसे करने वाला कोई ना हो, तब उस sentence में हमें living या non-living subject दिखाई देता है लेकिन उसका passive नहीं बन सकता है। ऐसी क्रियाएं happening verbs कहलाती हैं।
(When an action happens on its own; there is no one to do it, we see a living or non-living subject in that sentence but its passive cannot be formed. Such verbs are called happening verbs.)
For example-
मेरी कुर्सी टूट गयी। (My chair broke.)
उसका गुब्बारा उड़ गया। (His balloon flew away.
बंटी गिर गया। (Bunty fell down.)
इन वाक्यों का passive नहीं बनेगा क्योंकि ये सभी क्रियाएं अपने आप हुई हैं।
She speaks softly.
Softly- adverb of manner
He runs slowly.
Slowly- adverb of manner
इन दोनों sentences का passive नहीं बनेगा क्योंकि इन sentences में कोई object नहीं है। Softly और slowly adverbs हैं।
1. Active: He runs a shop.
a shop- object
Passive: A shop is run by him.
2. Active: She speaks the truth.
the truth- object
Passive: The truth is spoken by her.
3. Active: The government goes up the price daily.
Passive: The price is gone up daily.
Note- इस sentence में by the government लिखना ज़रूरी नहीं है क्योंकि यह बात understood है कि कीमतें सरकार ही बढ़ाती है।
इस sentence में ‘go’ का अर्थ जाना नहीं है बल्कि बढ़ना है। यह एक phrasel verb है। यहां go up का object दिया गया है इसलिए passive बनना possible हो पाया है।
Passive Voice का प्रयोग क्यों किया जाता है-
Active Voice के वाक्यों को Passive Voice में और passive voice के वाक्यों को Active Voice में सिर्फ बदलना आना काफी नहीं है। इसके साथ ही active Voice और passive voice का प्रयोग समझना भी जरूरी है।
( Just knowing how to change sentences of Active Voice to Passive Voice and sentences of Passive Voice to Active Voice is not enough. Along with this, it is also important to understand the usage of Active Voice and Passive Voice.)
Passive Voice में किसी वाक्य को बोलने की जरूरत निम्नलिखित परिस्थितियों में पड़ सकती है:
1. जब हमें कर्ता का पता ही ना हो कि काम किसके द्वारा किया गया है अर्थात क्रिया को करने वाला कौन है।
2. जब कर्ता से अधिक कर्म को महत्व दिया जाता है। जब कर्ता उतना ज्यादा महत्वपूर्ण ना हो जितना की कर्म है।
3. कर्ता कौन है यह परिस्थिति के अनुसार स्पष्ट होने के कारण कर्ता का उल्लेख करना आवश्यक न हो।
4. अगर कभी कर्ता का उल्लेख जानबूझकर टालना हो तब भी passive voice का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है।
(The need to speak a sentence in Passive Voice may arise in the following situations:
1. When we don’t know who is the doer of the action.
2. When the doer is not as important as the action.
3. Since it is clear as per the situation who the doer is, it is not necessary to mention the doer.
4. Passive voice can also be used if mention of the subject needs to be deliberately avoided.)
Some Important Points:
1. किसी वाक्य को Active Voice में बनाया जाए या Passive Voice में, इसका निर्णय इस बात पर निर्भर करता है कि हम किस पर ज्यादा जोर देना चाहते हैं- Doer of the action या फिर Receiver of the action जिस पर stress डालना हो उसे ही subject बना दिया जाता है। Stress change करने के लिए ही active to passive जाते हैं।
अगर किसी क्रिया को करने वाला ज्यादा Important है तो sentence active Voice में बनाया जाएगा और यदि क्रिया का प्रभाव जिस पर पड़ रहा है वह ज्यादा Important है तो sentence passive voice में बनाया जाएगा।
2. किसी sentence को passive voice में कहने की जरूरत हमें तभी पड़ती है जब हमें subject को mention ना करना हो। अगर Passive Voice में भी ‘by’ के द्वारा subject mention करना पड़े तब Active Voice में ही किसी बात को कहना ज्यादा comfortable है।
(Whether a sentence should be made in Active Voice or Passive Voice, its decision depends on what we want to emphasize more on- Doer of the action or Receiver of the action. The one on which the stress is to be put is made the subject. We go from active to passive only to change the stress.
If the person doing an action is more important then the sentence will be made in Active Voice and if the thing on which the effect of the verb is occurring is more important then the sentence will be made in passive voice.
2. We need to say a sentence in passive voice only when we do not have to mention the subject. If we have to mention the subject using ‘by’ even in passive voice, then it is more comfortable to say something in active voice.
Passive Voice without Agent
1. Unknown Agents
(One, someone, somebody, nobody, they, people, etc.)
जिन वाक्यों में हमारे पास अस्पष्ट noun या pronoun होता है वहां preposition ‘by’ का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता।
( In sentences where we have a VAGUE (unclear/unknown) noun or pronoun, the preposition ‘by’ is not used.)
Active: Somebody killed the dog.
Somebody- vague/ unclear pronoun
Passive: The dog was killed.✓✓✓
The dog was killed by somebody. ×××
(Due to the vague pronoun, it is wrong.)
Active: He killed the dog.
He- clear/ definite pronoun
Passive: The dog was killed by him.
Active: Somebody cut the telephone wire.
Somebody- indefinite pronoun
Passive: The telephone wire was cut.
Active: One should keep one’s promises.
One- vague/ unclear pronoun
Passive: Promises should be kept.
2. Understood Agents
(कुछ actions के agents निश्चित होते हैं।)
कुछ ऐसे action words होते हैं जिनके agents (doers) निश्चित होते हैं। उन्हें उन्हीं agents के द्वारा किया जाता है, किसी अन्य के द्वारा नहीं। जैसे- loot (डाका डालने) का काम robbers (लुटेरे) ही करते हैं। Arrest करने का काम पुलिस करती है। इस तरह के agents को भी passive voice में नहीं लिखा जाता हैं।
Examples-
Active: Police arrested the thieves.
Passive: The thieves were arrested.
Active: People speak English all over the world.
Passive: English is spoken all over the world.
Some More Cases Of Conversions From Active To Passive
1. जब एक prepositional verb Change होता है, active से passive voice में, तब preposition नहीं हटना चाहिए। जैसे-
Active: The committee is looking into the matter.
Passive: The matter is being looked into by the committee.
Active: They were laughing at me.
Passive: I was being laughed at by them.
2. None को anyone में और Nobody को anybody में change कर दिया जाता है और sentence को negative बनाने के लिए can के बाद ‘not’ का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
Note- not+any= None/nobody
None helps me.
I am helped by none. ×××
I am not helped by anyone.✓✓✓
None likes him.
He is liked by none. ×××
He is not liked by anyone. ✓✓✓
Nobody can do this.
This cannot be done by anybody.
3. जब verb Di transitive हो तब उस का दो तरह से passive बनाया जा सकता है क्योंकि दो object होते हैं।
(If we have two different objects, the passive can be made in two different ways.)
1. Active- I taught him cycling.
Passive- He was taught cycling by me.
Cycling was taught to him by me.
2. Active: The sun gives us light.
Passive: We are given light by the sun.
Light is given to us by the sun.
3. Active: He presented her a ring.
Passive: She was presented a ring by him./
A ring was presented to her by him.
Note- यहां दोनों object verb (present) के है इसीलिए दो तरह से passive बनाना possible हुआ।
He presented a ring to her.
A ring was presented to her by him.
( यहां एक object verb का है और एक object preposition का। इसीलिए इस sentence का दो तरह से passive नहीं बनाया जा सकता।)
Note-Passive voice में V3 के बाद अगर direct object रखा जाता है तो कोई preposition नहीं लगती।
Passive voice में V3 के बाद अगर Indirect object रखा जाता है तो उसके पहले ‘to’ का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
Double objects होने पर Indirect subject को preference दी जानी चाहिए Passive Voice का subject बनाने के लिए।
4. Position of ‘ever’ in Passive Voice
Active: Sahil doesn’t ever bother us.
Passive: We are not ever bothered by Sahil.
Note-(1) ‘not ever’ को Passive बनाते वक्त never में change नहीं करेंगे।
(2) Active में ‘ever’ bother से पहले है तो passive में भी ‘ever’ को bother से पहले रखेंगे।
5. Preposition- as well as and besides
Active: He has invited Abhishek as well as you.
Passive: Abhishek as well as you has been invited by him.
Active: He can speak English besides 5 other languages.
Passive: English besides 5 other languages can be spoken by him.
Note- ‘as well as, besides’ – ये दोनों भले ही preposition है पर इनके काम conjunction वाले होते हैं। इनसे जब दो चीजें जोड़ी जाती है तो passive बनाते वक्त उन्हें इकट्ठा ही रखना चाहिए। उन्हें अलग-अलग नहीं तोड़ना चाहिए।
6. Adjective phrase/ Adjective clause in Passive Voice
Adjectival phrase या adjectival clause को उस noun या pronoun के साथ ही लिखा जाता है जिसके लिए यह use किया गया है। किसी और स्थान पर रख देने से meaning change हो जाता है जबकि passive voice बनाते वक्त meaning हमेशा same रहना चाहिए।
Active: He taught the boy who was weak.
Passive: The boy who was weak was taught by him.
Who was weak- adjective clause
Active: Mr. Shamsher Singh was chasing the thieves that had stolen the car.
Passive: The thieves that had stolen the car were being chased by Mr. Shamsher Singh.
that had stolen the car- adjectival clause
Active: The man called the boy with red hair.
Passive: The boy with red hair was called by the man.
With red hair- adjective phrase
Note-Adjectival phrase का generally voice change नहीं किया जाता।
7. Causative verbs के sentences को passive में बनाते वक्त secondary verb को full infinitive में लिखा जाता है।
Active: The coach made the players practise hard.
Passive: The players were made to practise hard by the coach.
Active: He made you work.
Passive: You were made to work by him.
Note- Active Voice में make के साथ bare infinitive use होता है जबकि passive voice में made (V3) के साथ full infinitive (to+V3) use होता है।
8. Passive Voice में object complement का प्रयोग
(Use of object complement in passive voice)
Active: They elected him secretary.
Passive: He was elected secretary by them.
Note- ‘him and secretary’ एक ही व्यक्ति है, ये दो अलग-अलग object नहीं हैं। ‘him’ को ही secretary चुना गया। Secretary एक object complement है यानि ये ‘him’ के बारे में extra information दे रहा है।
Active: The team made Yash captain.
Passive: Yash was made captain.
Yash- real object
Captain- complement
Note-चूंकि captain एक complement है इसलिए सिर्फ Yash को ही subject बनाया जा सकता है, captain को नहीं। Complement का passive नहीं बनता है।
Captain के पहले ‘to’ preposition नहीं लगेगी क्योंकि captain यहां कोई object नहीं है बल्कि एक complement है।
Active: People called him a fool.
Passive: He was called a fool.
Active: We made him monitor.
Passive: He was made monitor
9. सार्वभौमिक सत्य/ सामान्य कथनों का passive
(Passive of universal truths/ general statements)
1. Active: The sun rises in the east.
Passive: It is said that the sun rises in the east./
It is known that the sun rises in the east.
2. Active: We all know that there is only one God.
Passive: It is known to us that there is only one God.
3. Active: Honesty is the best policy.
Passive: It is well said that honesty is the best policy.
10. Passive of Sentences with different prepositions
कुछ मामलों में हम ‘by’ के स्थान पर अन्य ‘prepositions’ का प्रयोग करते हैं।
(In some cases, we use some other prepositions instead of ‘by’.
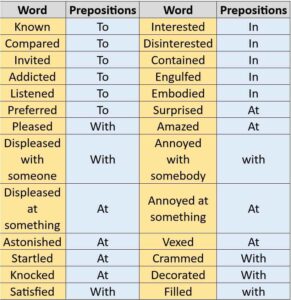
Examples-
Active: This bag contains many books.
Passive: Many books are contained in this bag.
Active: My answer didn’t satisfy him.
Passive: He was not satisfied with my answer.
Active: His behaviour shocked me.
Passive: I was shocked at his behaviour.
Active: Nisha knows me.
Passive: I am known to Nisha.
Active: He pleases you.
Passive: You are pleased with him.
Active: The fire engulfed the building.
Passive: The building was engulfed in the fire.
Active: The Constitution embodies human rights.
Passive: Human rights are embodied
किसी Sentence का Passive Voice बनाया जाना कब possible नहीं है
1. केवल Transitive Verbs का ही passive voice बनाया जा सकता है। Intransitive verbs का passive नहीं बनता।
( Only transitive verbs can be made into passive voice. Intransitive verbs cannot be made into passive voice.)
I am going to Delhi.
इस sentence का passive नहीं बनाया जा सकता क्योंकि ‘go’ एक Intransitive verb है।
go, come, laugh, weep, sleep, run, cry, sit, stand up, etc. –
ये सभी Intransitive Verbs हैं इसलिए इनका passive नहीं बनेगा।
She sat on the chair. (No passive)
He stood up. (No passive)
Chirag slept in the bed. (No passive)
Raju is coming to my home. (No passive)
2. State of being और state of possession के passive नहीं बनते है क्योंकि इनमें कोई action verb नहीं होती है।
( Passive of state of being and state of possession cannot be formed because there is no action verb in them.)
I have money.
इस sentence का passive nahi बनेगा क्योंकि इसमें possessive verb है जो कि state को show कर रही है। इसमें कोई action verb नहीं है।
The pen belongs to me. (No passive)
Passive बनाने के लिए verb transitive होनी चाहिए और इसमें कोई action verb होनी चाहिए।
Active: I have donated the money.
Donated- transitive verb
Passive: The money has been donated by me.
3. जिस sentence में object नहीं होगा, उस sentence का passive भी नहीं बनेगा।
( The passive of the sentence which does not have an object will not be formed.)
Change into passive-
Rahul went to school yesterday.
इस sentence का passive नहीं बनेगा क्योंकि इसमें कोई object ही नहीं है।
‘to school’ prepositional phrase है जो adverb of location का काम कर रहा है। Prepositional phrase कभी भी object नहीं हो सकता है। Object या तो noun होता है या objective pronoun.
Passive of Interrogative Sentences
Yes/No type Interrogative Sentences
1. Active: Do the boys read their books?
Passive: Are their books read by the boys?
Active: Does he write a letter?
Passive: Is a letter written by him?
Active: Is he repairing the roof?
Passive: Is the roof being repaired by him?
2. Active: Have you done this?
Passive: Has this been done by you?
Active: Did they solve it?
Passive: Was it solved by them?
Active: Were the teachers reading the books?
Passive: Were the books being read by the teachers?
Active: Was she not calling you?
Passive: Were you not being called by her?
Active: Shall I ever forget those happy days?
Passive: Will those happy days be ever forgotten by me?
Active: Will I have written a story by next month?
Passive: Will a story have been written by me by next month?
Interrogative Sentences Beginning with Wh Family Words
1. Active: Why do you like me?
Passive: Why am I liked by you?
2. Where do you read your book?
Where is your book read by you?
2. Active: How many books do you read?
Passive: How many books are read by you?
3. Active: How much water has he spent?
Passive: How much water has been spent by him?
Active: Why are you calling her?
Passive: Why is she being called by you?
Active: Where have you sent the parcel?
Passive: Where has the parcel been sent by you?
Active: Which teacher taught you?
Passive: By which teacher were you taught?
Active: Which man abused her?
Passive: By which man was she abused?
Active: What have you eaten today?
Passive: What has been eaten by you today?
Active: Where did he meet you?
Passive: Where were you met by him?
Active: How was she solving it?
Passive: How was it being solved by her?
Active: Where had they deposited the rupees?
Passive: Where had the rupees been deposited by them?
Look at the following sentences:
1. Active: Which song are you singing?
Passive: Which song is being sung by you?
2. Active: Which boy has broken the windows?
Passive: By which boy have the windows been broken?
Note- 1st sentence के passive में which song के साथ ‘by’ का use नहीं किया गया जबकि 2nd sentence के passive में which boy के साथ ‘by’ का use किया गया है। ऐसा क्यों?
आइये, समझते हैं इस बात को।
1st sentence में which song ‘object’ का कार्य कर रहा है जिसे passive voice बनाते वक्त ‘subject’ बना दिया गया है। ‘Subject’ के साथ ‘by’ preposition का use नहीं होता।
2nd sentence में which boy एक ‘subject’ का कार्य कर रहा है जिसे passive voice बनाते वक्त ‘by’ preposition का ‘object’ बना दिया गया है।
Active: What did he say?
Passive: What was said by him?
Active: What makes them happy?
Passive: By what are they made happy?
Or
What are they made happy by?
Note- Same thing यहां भी लागू होती है। 1st sentence में what ‘object’ है , he ‘subject’.
Passive बनाते वक्त what को subject बना दिया गया है और subject के साथ ‘by’ preposition का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता।
2nd sentence में what ‘subject’ का कार्य कर रहा है जिसे passive बनाते वक्त ‘by’ preposition का ‘object’ बना दिया गया है।
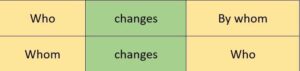
1. If the question begins with ‘who’-
Passive- (a) By whom+ auxiliary verb+subject+V3+?
(b) Who+ auxiliary verb+subject+V3+by+?
Active: Who wrote the Ramayana?
Passive: By whom was the Ramayana written?
Who was the Ramayana written by?
Active: Who was teaching him English?
Passive: By whom was he being taught English?/
Who was he being taught English by?
Active: Who asked you to draft this letter?
Passive: By whom were you asked to draft this letter?
2. If the question begins with whom-
Passive- Who+ auxiliary verb+V3+by+object?
अगर sentence whom से start हो तो उसका passive ‘who’ लगाकर बनायेंगे।
Active: Whom does he look for?
Passive: Who is looked for by him?
Active: Whom shouldn’t you invite to the party?
Whom- object (invite verb का), you- subject
Passive: Who shouldn’t be invited to the party by you?
Who- subject, you- object
Active: Whom did you laugh at?
Passive: Who was laughed at by you?
Note-Who का प्रयोग subject और object दोनों ही प्रकार से किया जा सकता है। जब who का प्रयोग object के रूप में किया जाता है तब इसके बाद helping verb और subject दोनों ही ज़रूर होते हैं।
Examples-
1. Active: Who are you waiting for?/
Whom are you waiting for?
Who/whom- object, you-subject
Passive: Who is being waited for by you?
2. Active: Who do you teach English?/
Whom do you teach English?
Who/whom- object, you- subject
Passive: Who is taught English by you?
3. Active: Who teaches you English?
Who-subject, you- object
Passive: By whom are you taught English?
4. Active: Who is waiting for you?
Who-subject, you- object
Passive: By whom are you being waited for?
Note- जब who का प्रयोग एक subject के रूप में किया जाता है (active voice में) केवल तभी उसे by whom में change करते है (passive voice में)।
और जब ‘who’ किसी sentence में object का कार्य करता है तब इसे who का who ही रहने देते है, कोई change नहीं करते।
Conclusion:
आशा करते है कि आपको ये आर्टिकल अच्छा लगा होगा और इस आर्टिकल की सहायता से आपको Passive Voice को समझने में काफी मदद मिली होगी। अगर आपके मन में कोई सवाल हो तो आप हमें नीचे कमेंट में पूछ सकते है। इस आर्टिकल को आप अपने मित्रों के साथ सोशल मीडिया पर शेयर जरुर करें।
Read More Posts:
Active Passive Voice Exercises
Active Passive Voice Exercises-Part 2
Active Passive Voice Exercises-Part 3