Learn all about Passive Voice of Modals(Passive voice- Part 2) and their usage in sentences.
Passive Voice-Part 2 -: Modal verbs are a category of auxiliary ( also called helping verbs) thaverbst express the mood or attitude of the speaker towards the action or state of the main verb in a sentence. These verbs indicate possibility, necessity, permission, ability, obligation, or likelihood. Often, we need to use modal verbs in passive voice sentences when the doer of the action is unknown, or unimportant, or when the focus needs to be shifted to the receiver of the action. In this article, we will explore how modal verbs and passive voice work together to create different sentence structures. We will also share rules and examples to enhance your understanding of this concept. So, let’s get started!
[ Modal verbs, auxiliary verbs की ही एक श्रेणी है (जिन्हें helping verbs भी कहा जाता है।) जो वाक्य में main verb के action या state के प्रति वक्ता के मूड या दृष्टिकोण को व्यक्त करती हैं। ये क्रियाएं संभावना, आवश्यकता, अनुमति, क्षमता या दायित्व को इंगित करती है। अक्सर हमें passive voice के वाक्यों में modal verbs का उपयोग करने की आवश्यकता होती है जब doer of the action अज्ञात या महत्वहीन होता है या जब receiver of the action पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने की आवश्यकता होती है। इस लेख में, हम यह पता लगाएंगे कि विभिन्न वाक्य संरचनाओं को बनाने के लिए modal verbs और passive voice एक साथ कैसे काम करती हैं। इस concept पर आपकी समझ को enhance करने के लिए नियम और उदाहरण भी साझा करेंगे। तो, चलिए शुरू करते हैं!]

Passive Voice Rules for modals-
The basic rules for converting active voice into passive voice are as follows:
1. The places of subject and object in a sentence are interchanged for converting active voice to passive voice.
2. Only 3rd form of the main verb of the active sentence is used as a main verb in passive voice.
3. To change sentences into passive voice, auxiliary verb ‘be’/ ‘been’ is added after the modal verb in a sentence according to their sense.
(Active voice को Passive voice में बदलने के मूल नियम इस प्रकार है:
1. Active voice को Passive voice में बदलने के लिए वाक्य में subject और object के स्थान को परस्पर बदल दिया जाता है।
2. Active voice की main verb की केवल 3rd form ही passive voice में main verb के रूप में प्रयोग की जाती है।
3. वाक्यों को passive voice में बदलने के लिए, सहायक क्रिया ‘be’/’been’ को वाक्य में उनके अर्थ के अनुसार modal के बाद जोड़ा जाता है।)
Auxiliary verb ‘be’ is used with these modals in Passive Voice- can, could, should, must, may, might, has to, had to, would, used to, ought to, would like to, etc.
With all the Modal Verbs with which the first form of the verb is used in Active Voice, BE is used in Passive Voice.
(जिन भी Modal Verbs के साथ Active Voice में Verb की First form का use होता है, उन सभी के साथ Passive Voice में BE का प्रयोग होता है|)
Object+ modal auxiliary verb+be+V3+by+subject.
The usage of auxiliary verbs in passive voice for Present & Future Modals is explained in the following table-
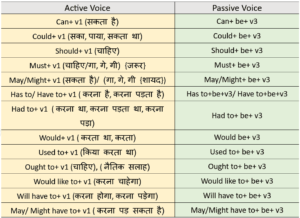
These structures allow us to express various ideas such as possibility, necessity, permission, etc., in passive voice. The passive voice is often used in formal texts.
Examples-
Active: He can pass this exam easily.
(वह यह परीक्षा आसानी से पास कर सकता है।)
Passive: This exam can be passed easily by him.
(यह परीक्षा उसके द्वारा आसानी से पास की जा सकती है।)
Active: I can solve your problem.
(मैं आपकी समस्या हल कर सकता हूं।)
Passive: Your problem can be solved by me.
(आपकी समस्या मेरे द्वारा हल की जा सकती है।)
Active: She can teach you English.
(वह आपको अंग्रेजी सिखा सकती है।)
Passive: You can be taught English by her.
(आपको उसके द्वारा अंग्रेजी सिखाई जा सकती है।)
Active: He could eat a mango.
(वह आम खा सका।)
Passive: A mango could be eaten by him.
(उसके द्वारा आम खाया जा सका।)
Active: You could not call him.
(आप उसे call नहीं कर पाए।)
Passive: He could not be called by you.
(उसे आपके द्वारा call नहीं किया जा सका।)
Active: Could you not compose it?
(क्या आप इसकी रचना नहीं कर पाए?)
Passive: Could it not be composed by you?
(क्या इसकी रचना आपके द्वारा नहीं की जा सकी?)
Active: Where should I write it?
(मुझे इसे कहां लिखना चाहिए?)
Passive: Where should it be written by me?
(इसे मेरे द्वारा कहां लिखा जाना चाहिए?)
Active: Students shouldn’t eat food during the class.
(विधार्थियों को कक्षा के दौरान खाना नहीं खाना चाहिए।)
Passive: Food shouldn’t be eaten during the class by students.
(कक्षा के दौरान विधार्थियों के द्वारा खाना नहीं खाया जाना चाहिए।)
Active: You should earn money.
(आपको पैसा कमाना चाहिए।)
Passive: Money should be earned by you.
(आपके द्वारा पैसा कमाया जाना चाहिए।)
Active: I must help my friend.
(मुझे अपने मित्र की मदद जरूर करनी चाहिए।)
Passive: My friend must be helped by me.
(मेरे मित्र की मदद मेरे द्वारा जरूर की जानी चाहिए।)
Active: You must obey the traffic rules.
(आपको यातायात के नियमों का पालन अवश्य करना चाहिए।)
Passive: The traffic rules must be obeyed.
(यातायात के नियमों का पालन अवश्य किया जाना चाहिए।)
Active: He must write a letter.
(वह पत्र अवश्य लिखेगा।)
Passive: A letter must be written by him.
( उसके द्वारा पत्र अवश्य लिखा जाएगा।)
Active: The management must reward him.
(प्रबंधन को उसे पुरस्कृत करना चाहिए।)
Passive: He must be rewarded by the management.
( उसे प्रबंधन द्वारा पुरस्कृत किया जाना चाहिए।)
Active: She may enjoy it.
( शायद उसे इसमें आनंद आए।)
Passive: It may be enjoyed by her.
(हो सकता है, उसके द्वारा इसका आनंद लिया जाए।
Active: They may offer her a new job.
(शायद वे उसे एक नई नौकरी की पेशकश कर सकते हैं।)
Passive: A new job may be offered to her by them.
(शायद उनके द्वारा उसे एक नई नौकरी की पेशकश की जा सकती है।)
Active: He may punish you for this negligence.
(वह इस लापरवाही के लिए आपको दंडित कर सकता है।)
Passive: You may be punished by him for this negligence.
(इस लापरवाही के लिए आपको उसके द्वारा दंडित किया जा सकता है।)
Active: He might kill the snake.
(वह सांप को शायद ही मार सकता है।)
Passive: The snake might be killed by him.
(उसके द्वारा सांप को शायद ही मारा जा सकता है।)
Active: He might beat you.
(वह शायद ही तुम्हें पीट सकता है।)
Passive: You might be beaten by him.
(उसके द्वारा तुम्हें शायद ही पीटा जा सकता है।)
Active: He might not help her.
(हो सकता है वह उसकी मदद न करे।)
Passive: She might not be helped by him.
( हो सकता है उसके द्वारा उसकी मदद ना की जाए।)
Active: She has to wash her clothes daily.
( उसे अपने कपड़े रोज़ धोने पड़ते है।)
Passive: Her clothes have to be washed by her daily.
( उसके कपड़े रोज़ उसके द्वारा धोये जाने पड़ते हैं।)
Active: You have to choose a dress.
( आपको एक पोशाक चुननी है।)
Passive: A dress has to be chosen by you.
( आपके द्वारा एक पोशाक चुनी जानी है।)
Active: You have to teach him everyday.
(आपको उसे हर रोज पढ़ाना है।)
Passive: He has to be taught by you everyday.
(उसे आपके द्वारा हर रोज पढ़ाया जाना है।)
Active: We had to file a case.
( हमें मामला दर्ज करना पड़ा।)
Passive: A case had to be filed by us.
(हमारे द्वारा मामला दर्ज किया जाना पड़ा।)
Active: She had to ask me.
(उसे मुझसे पूछना पड़ा।)
Passive: I had to be asked by her.
( उसके द्वारा मुझसे पूछा जाना पड़ा।)
Active: I would slap him.
(मैं उसे थप्पड़ मार देता।)
Passive: He would be slapped by me.
(उसे मेरे द्वारा थप्पड़ मार दिया जाता।)
Active: I would help you.
(मैं आपकी मदद करता।)
Passive: You would be helped by me.
( मेरे द्वारा आपकी मदद की जाती।)
Active: I used to read books.
(मैं किताबें पढ़ता था।)
Books used to be read by me.
(मेरे द्वारा किताबें पढ़ी जाती थी।)
Active: She used to speak Marathi.
(वह मराठी बोला करती थी।)
Passive: Marathi used to be spoken by her.
(उसके द्वारा मराठी बोली जाया करती थी।)
Active: We ought to respect our elders.
(हमें अपने बड़ों का आदर करना चाहिए।)
Passive: Our elders ought to be respected.
(हमारे बड़ों का सम्मान किया जाना चाहिए।)
Active: We ought to eat lots of fruit and vegetables everyday.
( हमें प्रतिदिन खूब सारे फल और सब्जियां खानी चाहिए।)
Passive: Lots of fruit and vegetables ought to be eaten everyday by us.
( हमारे द्वारा हर रोज खूब सारे फल और सब्जियां खाई जानी चाहिए।)
Active: We ought not to do this.
( हमें यह नहीं करना चाहिए।)
Passive: This ought not to be done by us.
( हमारे द्वारा यह नहीं किया जाना चाहिए।)
Active: I would like to teach English.
(मैं इंग्लिश पढ़ाना चाहूंगा।)
Passive: English would like to be taught by me.
( मेरे द्वारा इंग्लिश पढ़ाई जाना चाहेगी।)
Active: I would like to invite you.
( मैं आपको आमंत्रित करना चाहूंगा।)
Passive: You would like to be invited by me.
(आप मेरे द्वारा आमंत्रित किया जाना चाहेंगे।)
Active: They will have to check all documents.
(उन्हें सभी दस्तावेजों की जांच करनी होगी।)
Passive: All documents will have to be checked.
( सभी दस्तावेजों की जांच की जानी होगी।)
Active: I will have to cook food.
(मुझे खाना बनाना होगा।)
Passive: Food will have to be cooked by me.
(खाना बनाने काम मेरे द्वारा किया जाना होगा।)
Active: He may have to send you.
(हो सकता है उसे तुम्हें भेजना पड़े।)
Passive: You may have to be sent by him.
(तुम्हें उसके द्वारा भेजा जाना पड़ सकता है।)
Active: She might have to cancel her trip.
(उसे शायद अपनी यात्रा रद्द करनी पड़ सकती है।)
Passive: Her trip might have to be cancelled by her.
(हो सकता है उसके द्वारा यात्रा रद्द करनी पड़ जाए।)
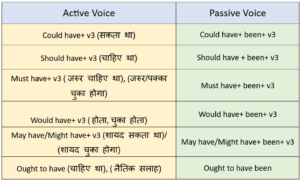
Auxiliary verb ‘been’ is used with these modals in Passive Voice- could have, should have, must have, would have, etc.
With all the Modal Verbs with which the 3rd form of Verb is used in Active Voice, BEEN is used in Passive Voice.
(जिन भी Modal Verbs के साथ Active Voice में Verb की 3rd form का use होता है, उन सभी के साथ Passive Voice में BEEN का प्रयोग होता है।)
Object+ modal auxiliary verb+ have+ been+ v3+ by+ subject.
The usage of auxiliary verbs in passive voice for Past Modals is explained in the following table-
 Examples-
Examples-
Active: They could have bought a new car.
( वे नई कार खरीद सकते थे।)
Passive: A new car could have been bought by them.
(उनके द्वारा एक नई कार खरीदी जा सकती थी।)
Active: I could have slapped him.
(मैं उसे थप्पड़ मार सकता था।)
Passive: He could have been slapped by me.
( उसे मेरे द्वारा थप्पड़ मारा जा सकता था।)
Active: She could have raised this matter in public.
( वह इस मामले को सार्वजनिक रूप से उठा सकती थी।)
Passive: This matter could have been raised by her in public.
(यह मामला उसके द्वारा सार्वजनिक रूप से उठाया जा सकता था।)
Active: She should not have broken the chair.
( उसे कुर्सी नहीं तोड़नी चाहिए थी।)
Passive: The chair should not have been broken by her.
( उसके द्वारा कुर्सी नहीं तोड़ी जानी चाहिए थी।)
Active: You should have helped her.
(तुम्हें उसकी मदद करनी चाहिए थी।)
Passive: She should have been helped by you.
(तुम्हारे द्वारा उसकी मदद की जानी चाहिए थी।)
Active: You should have spoken English.
( तुम्हें इंग्लिश बोलनी चाहिए थी।)
Passive: English should have been spoken by you.
(तुम्हारे द्वारा इंग्लिश बोली जानी चाहिए थी।)
Active: He must have eaten food.
(निश्चित ही वह खाना खा चुका होगा।)
Passive: Food must have been eaten by him.
(निश्चित ही उसके द्वारा खाना खाया जा चुका होगा।)
Active: Your father must have scolded you.
(तुम्हारे पापा ने पक्का तुम्हें डांटा होगा।)
Passive: You must have been scolded by your father.
(तुम्हें तुम्हारे पापा के द्वारा पक्का डांट पड़ी होगी।)
Active: I must have sent you.
(मुझे तुम्हें जरूर भेजना चाहिए था।)
Passive: You must have been sent by me.
(तुम्हें मेरे द्वारा जरूर भेजा जाना चाहिए था।)
Active: I must have sent you.
(मैंने तुम्हें जरूर भेजा होगा।)
You must have been sent by me.
(तुम्हें मेरे द्वारा जरूर भेजा गया होगा/ भेजा जा चुका होगा।)
Active: He would have purchased a car.
(उसने एक कार खरीद ली होती।)
Passive: A car would have been purchased by him.
( उसके द्वारा एक कार खरीदी जा चुकी होती।)
Active: You would have helped him.
(तुमने उसकी मदद की होती।)
Passive: He would have been helped by you.
(उसकी मदद तुम्हारे द्वारा की गई होती।)
Active: You would have done your work.
(आपने अपना काम किया होता।)
Passive: Your work would have been done by you.
(आपके द्वारा अपना काम किया गया होता।)
Active: They may have given him a book.
(उन्होंने शायद उसे किताब दी होगी।)
Passive: A book may have been given to him by them.
(उनके द्वारा शायद उसे कोई किताब दी गई होगी।)
Active: You may have eaten food.
(आप शायद खाना खा चुके होंगे।)
Passive: Food may have been eaten by you.
(आपके द्वारा खाना खाया जा चुका होगा।)
Active: She may have done her work.
(वह अपना काम कर चुकी होगी।)
Passive: Work may have been done by her.
(उसके द्वारा काम किया जा चुका होगा।)
Active: He might have broken this chair.
(शायद उसने इस कुर्सी को तोड़ा होगा।)
Passive: This chair might have been broken by him.
(यह कुर्सी शायद उसके द्वारा तोड़ी गई होगी।)
Active: She might have done her work.
(शायद ही उसने उसका काम किया होगा।)
Passive: Work might have been done by her.
(शायद ही उसके द्वारा काम किया गया होगा।)
Active: We ought to have respected those people.
(हमें उन लोगों की respect करनी चाहिए थी।)
Passive: Those people ought to have been respected by us.
(हमारे द्वारा उन लोगों की respect की जानी चाहिए थी।)
Active: We ought to have locked the gate.
(हमें गेट पर ताला लगा देना चाहिए था।)
Passive: The gate ought to have been locked by us.
(हमारे द्वारा गेट पर ताला लगा दिया जाना चाहिए था।)
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding and using the passive voice effectively, especially with modal verbs, is a key skill in English. It allows you to put emphasis on an action or an object, rather than the person performing it. This article has provided a comprehensive examination of the passive voice and modal verbs.
( निष्कर्ष में, passive voice को समझना और उसका प्रभावी ढंग से उपयोग करना, विशेष रूप से modal verbs के साथ, अंग्रेजी में एक महत्वपूर्ण कौशल है। यह आपको किसी action या object पर जोर देने की अनुमति देता है, न कि उसे करने वाले व्यक्ति पर। इस लेख में passive voice और modal verbs का विस्तृत परीक्षण किया गया है।)
Related Content:
Active Passive Voice Exercises
Active Passive Voice Exercises-Part 2
Active Passive Voice Exercises-Part 3
great article!
Great post!
Keep it up.