Today, we will take a look at the past modal verbs– should have, could have, and would have. These past tense modals are useful for expressing your present feelings about a past decision (or other action). Should have, could have, and would have are sometimes called ‘modals of lost opportunities.’
Meaning of past modals
Past modal verbs are used hypothetically, to talk about things that didn’t really happen in the past. These are used to talk about past possibilities, abilities, regrets, blame, deductions, or hypothetical situations.
(भूतकाल की modal verbs का प्रयोग काल्पनिक रूप से, उन चीजों के बारे में बात करने के लिए किया जाता है जो वास्तव में अतीत में नहीं घटी थीं। इनका प्रयोग अतीत की संभावनाओं, क्षमताओं, पछतावे, दोष, अनुमान या काल्पनिक स्थितियों के बारे में बात करने के लिए किया जाता है।)
Modal verb(should have/could have/would have)+ have+ past participle
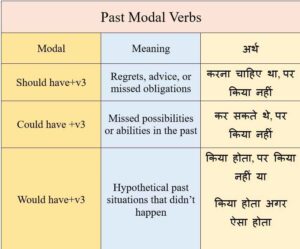
Three Main Types of Past Modals:
Each of these past modals has a slightly different meaning. We will look at each of them using examples.
1. Should have + past participle
Should have+V3 means that something did not happen, but we wished it had happened. We use “should have” to talk about past mistakes.
(Should have+V3 का मतलब है कि कुछ हुआ नहीं, लेकिन हम चाहते थे कि वह हो। हम पिछली गलतियों के बारे में बात करने के लिए “होना चाहिए था” का इस्तेमाल करते हैं।)
Examples-
They should have invited her to the party.
We should have booked the tickets earlier.
You should have told me you were running late.
She should have taken the job. It was perfect for her.
He should have told me that they cancelled the conference.
You should have told me you were going to bring someone.
I got a speeding ticket. I should have driven a bit more slowly.
Shouldn’t have+ past participle
The addition of ‘not’ reverses the meaning: it was a bad idea to do something, but you did it anyway.
(‘नहीं’ जोड़ने से अर्थ उलट जाता है: कुछ करना एक बुरा विचार था, लेकिन आपने फिर भी इसे किया।)
Examples-
I should not have yelled at him.
We should not have tried to fix the car ourselves.
They shouldn’t have ignored the warning signs.
2. Could have+ past participle
Could have+V3 means that something was possible in the past, or you had the ability to do something in the past, but that you didn’t do it.
(Could have+V3 का अर्थ है कि अतीत में कुछ संभव था, या अतीत में आपके पास कुछ करने की क्षमता थी, लेकिन आपने ऐसा नहीं किया।)
Examples-
They could have arrived earlier if they had taken a cab.
I could have helped you, but you didn’t ask.
We could have stayed longer, but we decided to leave.
They could have won the race, but they didn’t try hard enough.
I could have gone to the gym, but I wanted to sleep in.
The boy could have run away from the bullies, but he decided to confront them.
She could have recovered faster if she had followed the doctor’s advice.
Could have+v3- When we want to make a guess about something that happened in the past. In this case, we don’t know if what we are saying is true or not. We are just talking about our opinion of what may be happened.
(जब हम अतीत में घटी किसी घटना के बारे में अनुमान लगाना चाहते हैं, तो भी could have+V3 का प्रयोग करते है। इस स्थिति में, हमें नहीं पता कि हम जो कह रहे हैं वह सच है या नहीं। हम बस अपनी राय बता रहे हैं कि क्या हुआ होगा।)
Examples-
Are you crazy? We could have gotten into an accident!
Why is Peter late? He could have got stuck in traffic.
I’ve lost my keys; I could have left them at work.
Couldn’t have+ past participle
Could not have+ V3 means that something wasn’t possible in the past, even if you had wanted to do it.
(Could not have+V3 का अर्थ है कि अतीत में कुछ संभव नहीं था, भले ही आप इसे करना चाहते थे।)
(Opposite to could have: something was hypothetically impossible.)
Examples-
He couldn’t have done it without your help.
I checked the equipment many times, it couldn’t have failed.
I couldn’t have arrived any earlier. There was a terrible traffic jam.
3. Would have+ past participle
Would have+v3- we use “would have” to imagine a result (if something had been different in the past).
[हम would have+V3 का प्रयोग परिणाम की कल्पना करने के लिए करते हैं (यदि अतीत में कुछ अलग हुआ होता।)]
(It has the same meaning as in the third conditional sentences.)
Examples-
We would have gone hiking, but the weather was bad./
If the weather had been good, we would have gone hiking.
They would have won the game if they had practiced more.
If we had arrived earlier, we would have caught our flight.
If I had brought my umbrella, I wouldn’t have got wet in the rain.
Would have+ v3- we can also use would have+V3 to talk about something you wanted to do but didn’t.
(हम would have+V3 का उपयोग किसी ऐसी बात के बारे में बात करने के लिए भी कर सकते हैं जिसे आप करना चाहते थे लेकिन नहीं कर पाए।)
Examples-
I would have called you, but I didn’t know your number.
I would have come to meet you, but I was getting late.
You would have passed the exam if you had studied harder.
Had you invited me, I would have definitely come.
Wouldn’t have+v3
It is used to express regret or discuss hypothetical outcomes that didn’t happen.)
(इसका प्रयोग खेद व्यक्त करने या ऐसे काल्पनिक परिणामों पर चर्चा करने के लिए किया जाता है जो घटित नहीं हुए।)
Examples-
If I had texted her, she wouldn’t have replied.
If we had arrived earlier, we wouldn’t have missed our train.
I wouldn’t have got this job if I hadn’t met Mr. Sharma.
Conclusion:
अगर आपको ये आर्टिकल (Past Modal Verbs- Part 1) पसंद आया हो, तो इसे अपने Friends और other students के साथ share अवश्य करें।
Related Posts-
How to use ‘Used to’ in English Grammar